From Raw Material to Precision Component: a Deep Dive Into Screw Manufacturing Process
One might argue that the process of manufacturing screws is a mundane and unremarkable task. However, upon closer examination, it becomes evident that screw manufacturing is a complex and intricate process that involves various steps from raw material to precision component.
This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of the screw manufacturing process, delving into its historical background, common materials used, design considerations, contemporary production methods, quality assurance practices, and analysis of adverse phenomena.
By examining this often overlooked aspect of industrial production, we can gain a deeper understanding of the significance and intricacies behind the creation of precision components like screws.
1. History of Screw Manufacturing
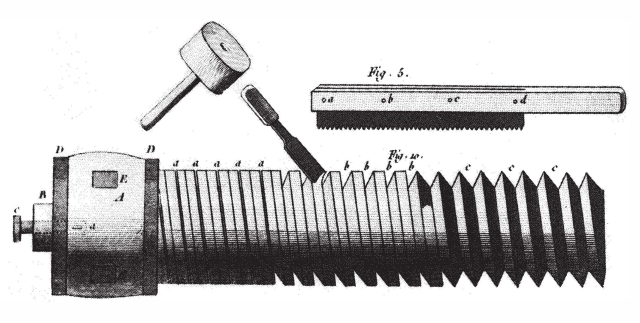
The history of screw manufacturing can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where rudimentary versions of screws were used in various applications. The earliest evidence of screws dates back to Ancient Egypt, where wooden screw-like devices were found in tombs dating as early as 2500 BCE. These early screws were primarily used for pressing grapes and olives, as well as extracting water from mines. The concept of the screw was further developed by the Greeks and Romans, who used it for irrigation systems and presses.
During the Middle Ages, screws saw limited use due to their complexity and high cost of production. However, with the advent of industrialization in the 18th century, advancements in metalworking techniques allowed for mass production of screws. This led to increased adoption of screws across industries such as construction, machinery, and transportation.
The development of standardized thread profiles by engineers like Sir Joseph Whitworth in the mid-19th century further revolutionized screw manufacturing. This enabled interchangeability between different components and facilitated easier maintenance and repair.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about common materials of screws: As technology progressed and demand grew over time, manufacturers began experimenting with different materials for screw production.
2.Common materials of screws

Commonly used materials for screws include steel, stainless steel, brass, and nickel alloys. These materials are selected based on their specific properties and the requirements of the application. Steel is a popular choice due to its strength and durability. Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications in harsh environments. Brass is commonly used for decorative screws due to its aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance. Nickel alloys provide superior strength, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance compared to other materials.
Steel: Known for its high tensile strength and durability.
Stainless steel: Offers excellent corrosion resistance in various environments.
Brass: Provides an attractive appearance along with good corrosion resistance.
The selection of material plays a crucial role in determining the performance and longevity of a screw. Once the appropriate material has been chosen, engineers can proceed to design the screw structure that meets specific application requirements. This transition from material selection to screw design marks the beginning of exploring 'the art of screw design', where factors such as thread pitch, diameter, length, head style, drive type come into play to create an efficient fastening solution.
Mikehardware will help you find the best solution for your Screws material!
3.The Art of Screw Design
Engineers employ various design parameters, such as thread pitch, diameter, length, head style, and drive type, to create efficient fastening solutions during the art of screw design. These design parameters are carefully considered to ensure that the screw can effectively fulfill its intended purpose while also being compatible with the materials it will be used on.
The thread pitch determines the distance between each thread and affects how tightly the screw can hold materials together. Diameter and length play a crucial role in determining the strength and stability of the screw. Head style is chosen based on aesthetic appeal or functional requirements such as flushness or easy removal. Drive type refers to the shape of the recessed area that allows a tool to engage with the screw for installation or removal.
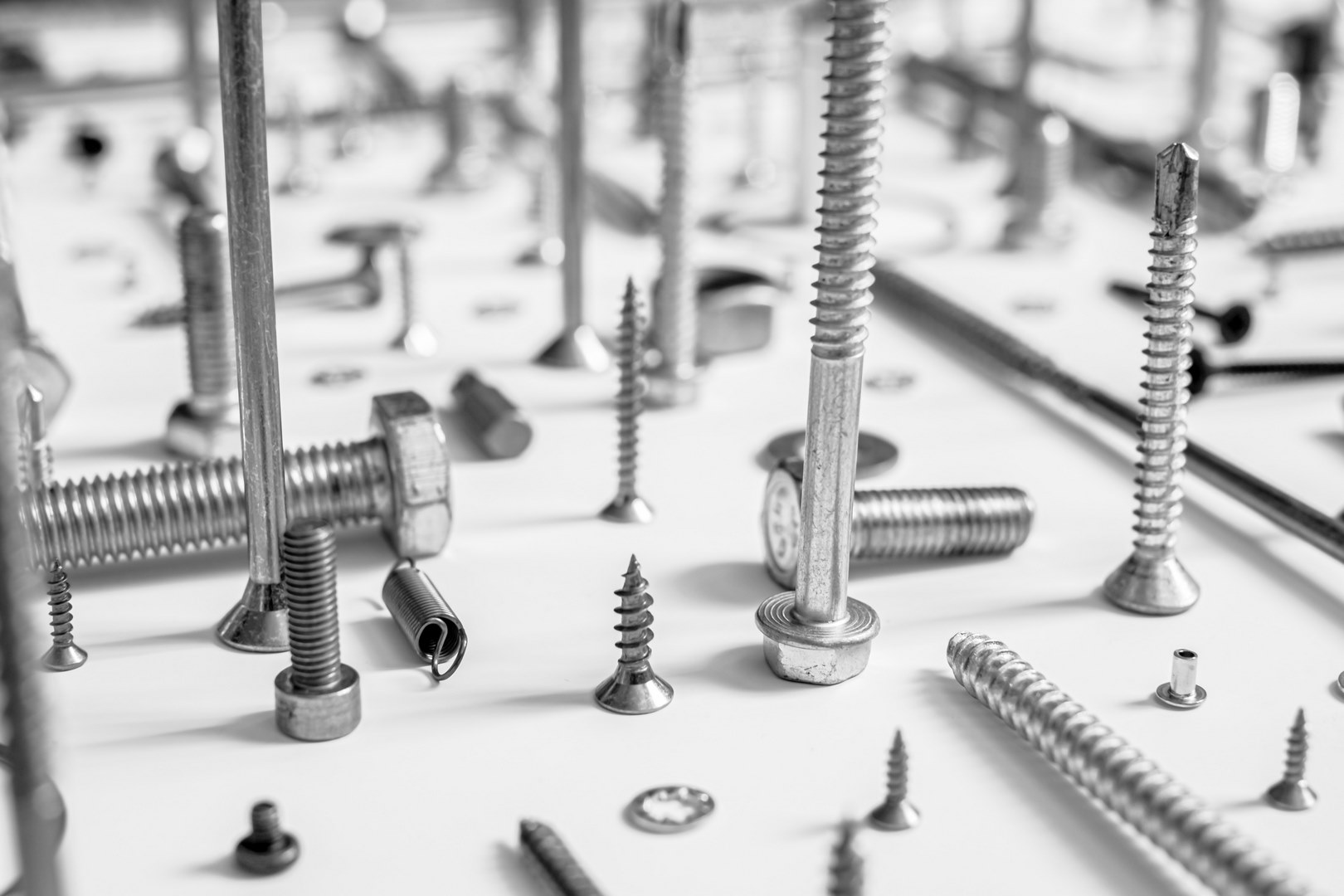
The process of manufacturing screws today involves several steps that transform raw material into precision components. This process includes material selection, cold heading (where wire is cut into blank form), forming threads through rolling or cutting processes, heat treatment for increased strength and durability, surface finishing (such as plating or coating), and final inspection for quality assurance. Each step in this process is essential in producing high-quality screws that meet industry standards and customer expectations.
4.The process of manufacturing screws Today

The Journey From Raw Material To Functional Screw
One important aspect of contemporary screw production involves a series of steps that ensure the creation of high-quality screws that meet industry standards and customer expectations. These steps include:
- Material Selection: The first step in screw manufacturing is selecting the appropriate material for the desired application. Different materials, such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or brass, have different properties that affect the performance and durability of the screws.
- Cold Heading: Once the material is chosen, it undergoes a process called cold heading. During this step, a metal wire is cut into a specific length and then formed into the shape of a screw head using high-pressure dies. This process ensures precise dimensions and consistent quality.
- Thread Rolling: After cold heading, thread rolling takes place to create threads on the shaft of the screw. This process involves pressing the screw against rotating dies to form accurate threads with high tensile strength.
These steps in contemporary screw production contribute to producing screws with excellent quality assurance and reliability. By carefully selecting materials, utilizing cold heading techniques, and performing thread rolling accurately, manufacturers can ensure that their screws meet industry standards and provide reliable performance for various applications.
Contact us now for a deeper dive into the world of screw production!
5.Quality Assurance and Reliability

Quality assurance and reliability are key considerations in contemporary screw production. Manufacturers employ rigorous quality control measures throughout the manufacturing process to guarantee the integrity of their products. These measures include thorough material inspections, dimensional checks, and mechanical testing.
One important aspect of quality assurance is the inspection of raw materials used in screw production. Materials must meet specific requirements in terms of chemical composition, mechanical properties, and surface finish. This ensures optimal performance and longevity of the finished product. Dimensional checks are also conducted at various stages of production to verify that screws adhere to precise specifications. This involves measuring critical dimensions such as thread diameter, pitch, length, and head shape.
Mechanical testing is another crucial step in quality assurance. It involves subjecting samples or representative batches of screws to various stress conditions to assess their strength and durability. Common tests include tensile strength testing, torque resistance testing, and corrosion resistance testing.
By implementing these quality control measures, manufacturers can identify any defects or deviations from the required standards early on and take corrective actions. This ensures that customers receive reliable screws that meet or exceed their expectations.
Transition: Understanding the importance of maintaining high-quality standards in screw production leads us to analyze the causes of any potential issues that may arise during the forming process.
6.Q&A In The Screws Production Process

Manufacturing screws involves various processes, and several problems can arise during each stage of production. Identifying and addressing these issues is crucial to ensure the production of high-quality screws. Here are some common problems that may occur during the screw production process and how to analyze them:
Material Quality Issues:
Problem: Poor quality raw materials can lead to screws with reduced strength or durability.
Analysis: Regularly inspect incoming material quality and perform material testing to identify any defects or inconsistencies.
Inconsistent Dimensions:
Problem: Variations in the screw dimensions, such as length, diameter, or thread pitch, can lead to compatibility issues.
Analysis: Implement stringent quality control measures, including using precision instruments to measure dimensions and conducting statistical process control (SPC) to monitor variations.
Thread Quality Problems:
Problem: Inadequate thread quality can result in poor threading, difficulty in screwing, or reduced holding power.
Analysis: Use thread gauges to verify thread quality and implement regular inspections during production. Adjust machine settings as needed to maintain thread quality.
Surface Finish and Coating Issues:
Problem: Inconsistent surface finish or coating can affect the screw's appearance and corrosion resistance.
Analysis: Perform visual inspections and conduct tests for coating thickness and adhesion. Maintain proper coating equipment and processes.
Heat Treatment Problems:
Problem: Improper heat treatment can lead to screws with inadequate hardness, making them prone to breakage or deformation.
Analysis: Monitor heat treatment processes, ensure proper quenching and tempering, and conduct hardness testing to verify compliance with specifications.
Continuous monitoring, data collection, and analysis are essential for identifying and addressing these problems in the screw manufacturing process. Implementing quality control and quality assurance procedures is vital to producing high-quality screws consistently.
7.Guidelines and Models

Guidelines and models for improving the common rolling process are essential in order to optimize operations, minimize defects, and achieve higher levels of precision. These guidelines provide a systematic approach to enhance the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the rolling process. By following these guidelines, manufacturers can ensure that each step of the process is carried out with precision and accuracy.
Selection of suitable raw materials: The choice of raw materials plays a crucial role in determining the quality of the final product. Guidelines help manufacturers select raw materials that possess the necessary characteristics required for successful common rolling.
Optimization of rolling parameters: Various parameters such as temperature, pressure, and speed have a significant impact on the outcome of the rolling process. Guidelines provide models that enable manufacturers to determine optimal parameter settings for achieving desired results.
Quality control measures: Continuous monitoring and inspection throughout the rolling process are vital to identify any potential defects or deviations from specifications. Guidelines outline quality control measures that ensure adherence to predefined standards.
These guidelines not only improve operational efficiency but also contribute to reducing wastage, enhancing productivity, and producing components with higher precision. Manufacturers who follow these guidelines can achieve consistent results while minimizing variability in their production processes.
In conclusion, the process of screw manufacturing is a fascinating journey from raw material to precision component. Throughout history, screws have evolved alongside advancements in technology and materials.
The design of screws requires careful consideration of factors such as thread shape and pitch. Modern manufacturing processes ensure high-quality and reliable screws for various applications.
However, there are occasional adverse phenomena that can occur during the forming process, which require analysis and troubleshooting.
By following guidelines and models, manufacturers can continue to produce efficient and durable screws that play an essential role in countless industries.
Ready to Elevate Your Screw Solutions?
Contact us now for a FREE QUOTE of perfect custom screws and fasteners for your needs!





