How Fasteners Are Made From Raw Materials to Finished Products
How are fasteners transformed from raw materials into finished products?
This article examines the process of fastener manufacturing, starting with a general introduction to the topic.
It then delves into the historical context of industrial revolution and early techniques employed in the production of fasteners.
Subsequently, advancements in materials used for fastener production are discussed, followed by an exploration of various modern manufacturing methods.
1. General Introduction about Fasteners
Fasteners are essential components in custom metal part hardware. They encompass a wide range of devices, such as screws, bolts, nuts, and rivets, designed to securely join materials together. Fasteners play a critical role in ensuring structural integrity, stability, and functionality of various products, from machinery to electronics. They come in diverse materials, sizes, and configurations to accommodate specific needs.
Our Mikehardware custom metal part hardware manufacturing expertise includes producing high-quality fasteners that meet precise specifications, contributing to the reliability and longevity of assembled components across industries.
2. Industrial Revolution And Early Techniques
During the Industrial Revolution, early techniques were developed for the manufacturing of mechanical joining devices. These techniques played a crucial role in shaping the fastener industry as we know it today. Here are some key aspects of these early techniques:
- Manual Production: Fasteners were initially produced by skilled craftsmen who meticulously crafted each piece by hand. This labor-intensive process required a high level of precision and attention to detail.
- Blacksmithing: Blacksmiths played a significant role in producing fasteners during this era. They used traditional forging methods to shape and mold metal into various types of fasteners, such as nails, bolts, and screws.
- Limited Machinery: Early factories relied on basic machines like drop hammers and power presses to assist in the production process. However, these machines had limited capabilities compared to modern-day manufacturing equipment.
- Small-Scale Operations: Fastener production during this period was primarily carried out in small workshops or cottage industries. These establishments often employed local craftsmen who worked together using rudimentary tools.
These early techniques laid the foundation for advancements in materials that would revolutionize the fastener industry. Without these initial developments, subsequent progress would not have been possible.
3. Advancements in Materials

Significant progress in the fastener industry was achieved through the development of innovative materials that brought about a revolution in manufacturing techniques. The introduction of new materials with improved properties, such as strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, allowed for the production of more efficient and reliable fasteners. These advancements not only enhanced the performance of fasteners but also expanded their range of applications.
One notable development in fastener materials is the use of stainless steel. This alloy offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it highly suitable for applications in harsh environments or exposed to moisture. Stainless steel fasteners are widely used in industries such as construction, automotive, and aerospace.
Another significant advancement is the utilization of titanium alloys. These alloys possess exceptional strength-to-weight ratios along with excellent corrosion resistance. As a result, titanium fasteners find extensive applications in industries where weight reduction is critical, such as aviation and racing.
In addition to stainless steel and titanium alloys, other specialized materials have been developed for specific purposes. For example, nickel-based superalloys are utilized when high-temperature resistance is required.
The table below summarizes some key materials used in modern fastener production:
| Material | Properties | Applications |
| Stainless Steel | High corrosion resistance | Construction, automotive |
| Titanium Alloys | High strength-to-weight ratio | Aerospace, racing |
| Nickel-Based Superalloys | High-temperature resistance | Gas turbines |
These advancements in materials have paved the way for further innovations in manufacturing methods for fasteners.
4.Manufacturing Methods

Advancements in manufacturing methods have played a crucial role in improving the efficiency and reliability of fasteners. These advancements have revolutionized the production process, allowing for faster and more accurate manufacturing. Here are some key aspects of modern manufacturing methods:
- Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines: These automated machines use pre-programmed software to control the movement of tools, resulting in precise cutting, shaping, and forming of fasteners.
- High-speed production lines: Fastener manufacturers have implemented high-speed production lines that can produce a large number of fasteners in a short period. This not only increases productivity but also ensures consistent quality throughout the production process.
- Multi-stage heat treatment processes: Heat treatment is an essential step in enhancing the mechanical properties of fasteners. Modern manufacturing methods incorporate multi-stage heat treatment processes to achieve desired strength, hardness, and durability.
- Quality control systems: To ensure reliability and consistency, manufacturers employ advanced quality control systems. These systems utilize technologies such as computer vision and automated inspection techniques to detect any defects or deviations from specifications.
These advancements in manufacturing methods have significantly improved the speed, accuracy, and quality of fastener production.
In the subsequent section about modern manufacturing processes of bolts, screws, and fasteners without writing 'step', we will explore these methods further.
5.Modern Manufacturing Processes of Bolts, Screws, And Fasteners
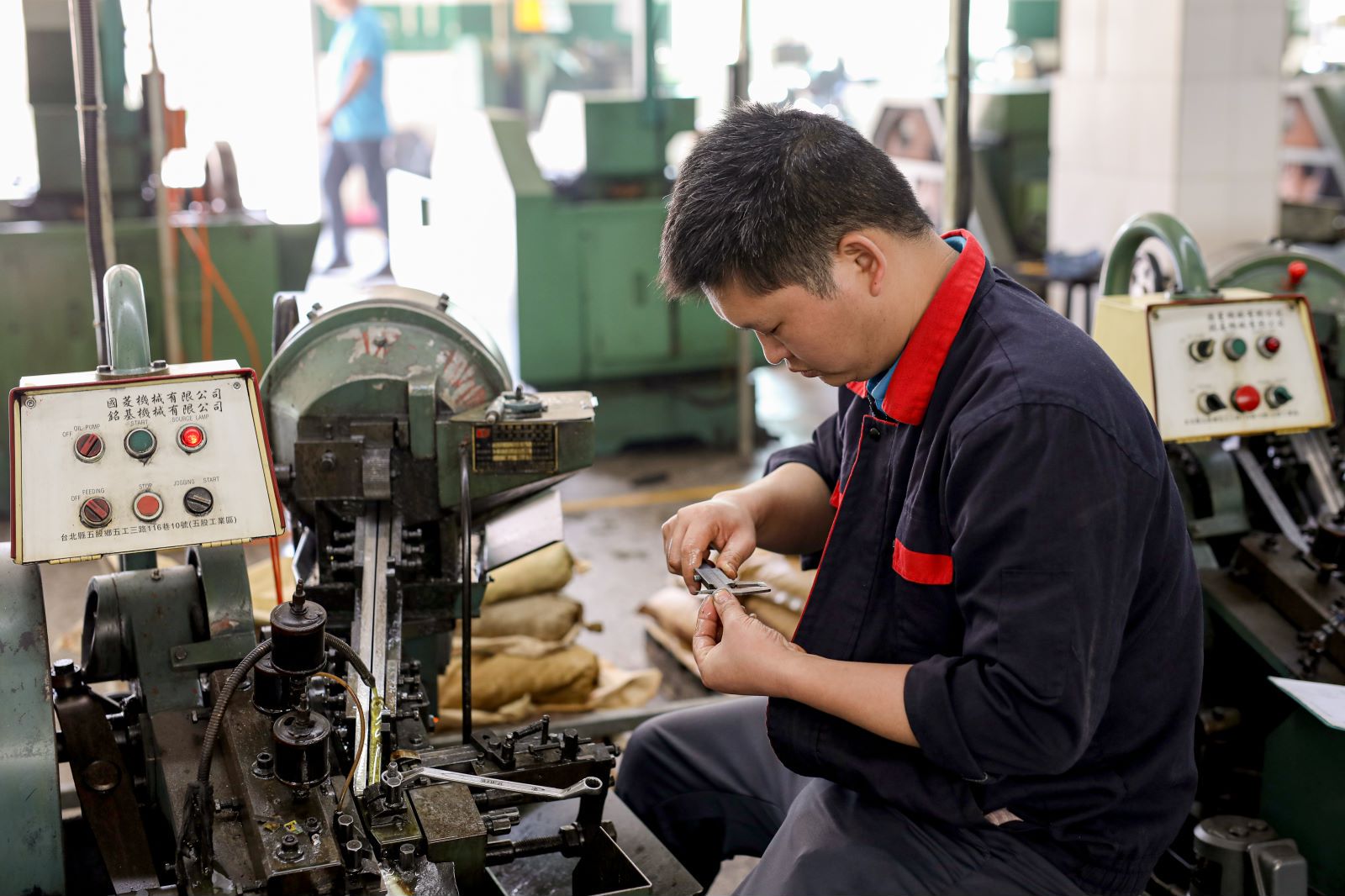

These processes combine advanced technology and precision craftsmanship to ensure the reliability and performance of our products.
Cold Heading: Our primary method involves cold heading, where metal wire is cut to length and then shaped using dies under high pressure. This forms the head and threads in a single operation, optimizing strength and integrity.
Thread Rolling: For threaded fasteners, we utilize thread rolling. This process involves pressing a hardened die against a blank to form the threads, resulting in increased strength and smoother surface finish compared to traditional threading.
Heat Treatment: We subject the fasteners to controlled heat treatment processes like quenching and tempering. This enhances their mechanical properties, such as strength, hardness, and resilience, ensuring they meet or exceed industry standards.
Surface Coating: To enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetics, we apply various surface coatings like zinc plating, galvanizing, or applying organic coatings. These coatings prolong the life of the fasteners, particularly when used in challenging environments.
Material Innovation: We stay updated with the latest materials, including advanced alloys and composites, to enhance the performance and durability of our fasteners, especially in demanding applications.
Customization: We offer a wide range of customization options, from sizes and materials to special coatings and designs. This ensures our fasteners meet the unique needs of our clients' projects.
Contact us for a free quote for customizing your business fasteners!
At Mikehardware, our modern manufacturing processes ensure that our bolts, screws, and fasteners are not only reliable but also contribute to the overall quality and longevity of the products in which they're used.
6.Environmental Considerations

One crucial aspect of modern manufacturing processes is the consideration of environmental factors, including waste reduction, resource conservation, and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions. In the production of fasteners, manufacturers have adopted various strategies to minimize their environmental impact. These include:
- Implementing recycling programs: Manufacturers are increasingly implementing recycling programs within their facilities to reduce waste generation. By collecting and reusing scrap materials such as metal shavings or excess raw materials, companies can minimize the amount of waste sent to landfills.
- Optimizing energy usage: Energy-intensive processes in fastener manufacturing can contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. To mitigate this impact, manufacturers are adopting energy-efficient technologies and practices. This includes utilizing advanced machinery with lower energy consumption and optimizing production schedules to reduce idle time and energy wastage.
- Water conservation measures: Fastener production often involves water-intensive processes such as cooling or cleaning operations. To conserve water resources, manufacturers are implementing measures like water recycling systems or using alternative cooling methods that require less water.
- Sustainable sourcing: Raw material selection plays a crucial role in reducing the environmental footprint of fasteners. Manufacturers are increasingly opting for sustainable sourcing practices by procuring materials from certified suppliers who adhere to responsible extraction methods.
Considering these environmental considerations, it is evident that manufacturers in the fastener industry are actively taking steps towards sustainable production practices.
Nevertheless, future trends will continue to push for even greater advancements in environmentally-friendly manufacturing processes without compromising quality or efficiency.
7.Future Trends

To address the challenges of sustainability in manufacturing, research and development efforts are focused on finding innovative solutions that minimize environmental impact while maintaining product quality and efficiency. As future trends emerge, it is becoming increasingly important to explore new technologies and processes for the production of fasteners.
One such trend is the use of renewable materials in manufacturing. Biomaterials derived from organic sources such as waste products have gained attention for their potential to reduce reliance on non-renewable resources. These materials can be used to create fasteners with comparable strength and durability to traditional options.
Another emerging trend is the adoption of additive manufacturing or 3D printing in fastener production. This technology allows for precise customization, reducing material waste and energy consumption compared to conventional manufacturing methods. Additionally, 3D printing enables complex geometries that were previously unattainable with traditional techniques.
Furthermore, advancements in automation and robotics are revolutionizing fastener manufacturing processes. Automated systems can increase productivity, reduce errors, and optimize resource utilization by streamlining operations.
In conclusion, the evolution of fastener manufacturing has been a remarkable journey from simple tools to complex engineered components. As the industrial revolution propelled us forward, early techniques laid the foundation for the sophisticated methods we employ today. The integration of advanced materials, precise manufacturing processes, and innovative technologies ensures that bolts, screws, and fasteners play a pivotal role in diverse industries.
Contact us to know more about custom or manufacturing fasteners products!





